Research: biomechanics
I am one of the main developers of the YALES2BIO solver, which is a numerical platform developed at the IMAG (with the aid of CORIA) to compute blood flows. It is based on the YALES2 solver, developed at CORIA notably by Dr. V. Moureau, researcher at CNRS. At the IMAG, we use the YALES2BIO solver for applications both at the macroscopic scale and at the microscopic scale.
Numerical simulation of cardiovascular flows with YALES2BIO
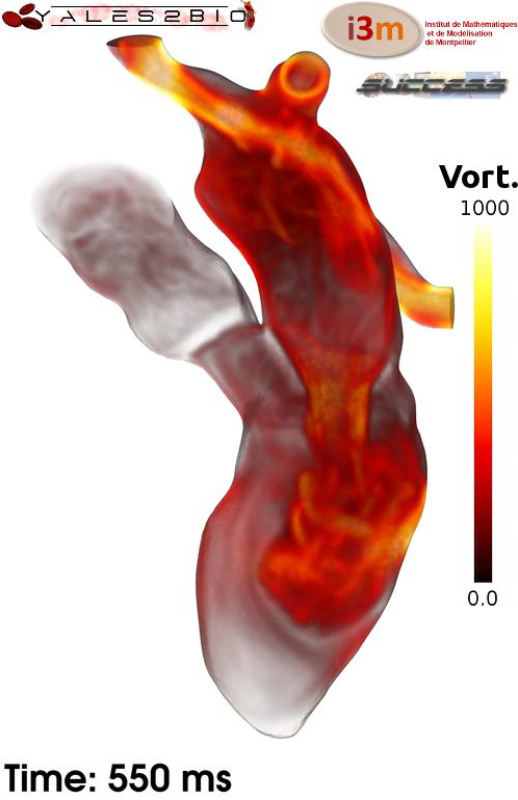
One of our main macroscopic applications is the computation of the flow in patient-specific left hearts. The principle of our method is based on the OCFIA chain. Thanks to a fellowship from CNRS, Christophe Chnafa, former PhD candidate at IMAG, has developed a numerical method able to reconstruct from medical images the geometry of the left heart cavities, and their movement along the cardiac cycle. Then, the prescribed-movement left heart is meshed and the flow in the moving domain is solved by YALES2BIO using an arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) technique. This method has been employed both on 4-D scan and MRI images. The immersed boundary method is used to account for the mitral and aortic valves. In addition of recovering the usual characteristics of the left heart flow, our first results show the presence of cycle-to-cycle variations and weak turbulence at different locations along the cardiac cycle.
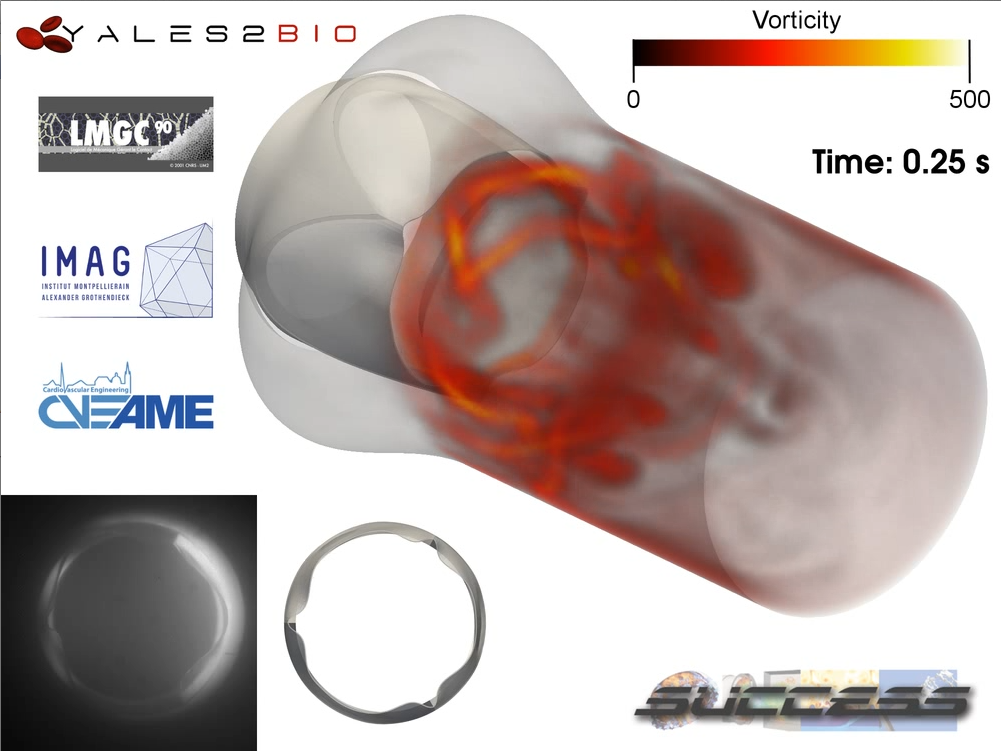
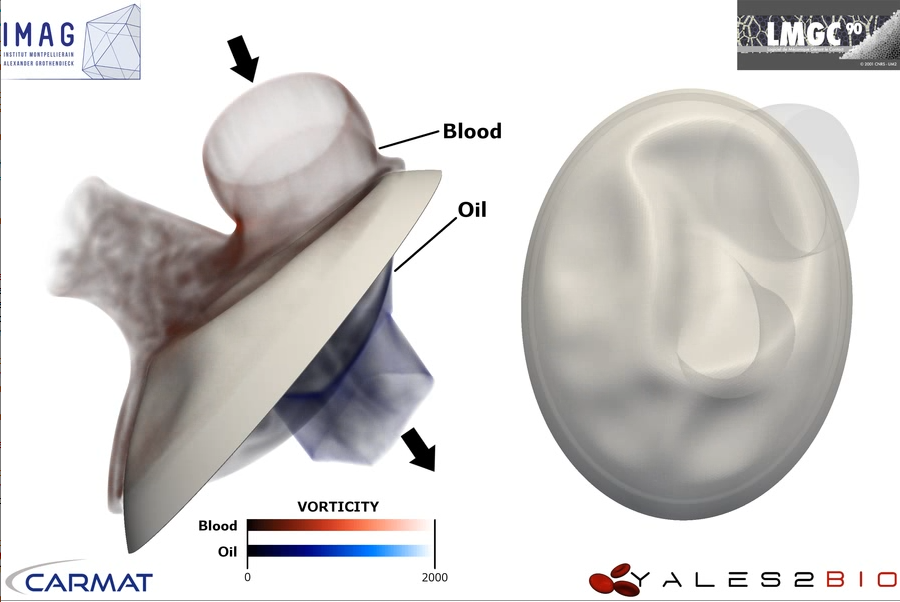
We also developed in YALES2BIO a method for the prediction of fluid-structure interaction in blood flows, in the thesis of Julien Siguenza. I show here simulations of the flow through an artificial aortic valve and in part of the artificial heart of the CARMAT company (internship of A. Larroque).
Numerical simulation of flows of red blood cells with YALES2BIO
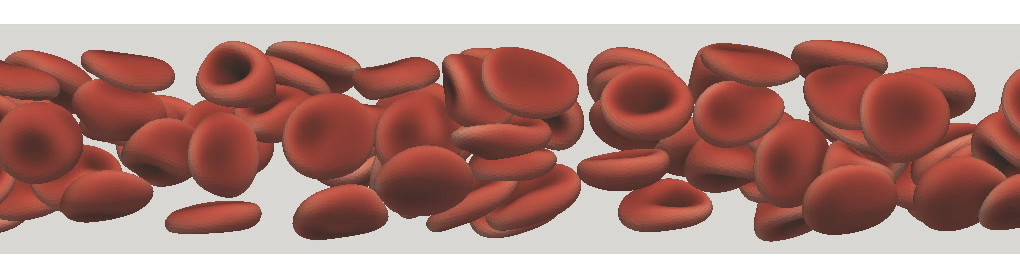
I am using YALES2BIO to perform simulations of deformable particles through fluid-structure interaction. We use a front-tracking immersed boundary method adapted for unstructured meshes. Our main application is the prediction of the dynamics of red blood cells.
SOme additional computations can be found on the YALES2BIO web page.
Current projects, grants and fellowships
-
The IMAG is part of the RHEOBLOOD project, funded by the NUMEV labex of Montpellier. This project gathers 11 institutions mainly from the Montpellier site. The objective of the project is to contribute to the understanding of blood rheology.
-
In 2016, we started a CIFRE PhD project with Horiba Medical on the simulation of red blood cell dynamics in blood analyzers.
-
In 2016, we also started a CIFRE PhD project with ALARA Expertise on the quality control of 4D MRI velocimetry.
-
We are starting a project with Sim and Cure for the simulation of flow in cerebral aneurysms.